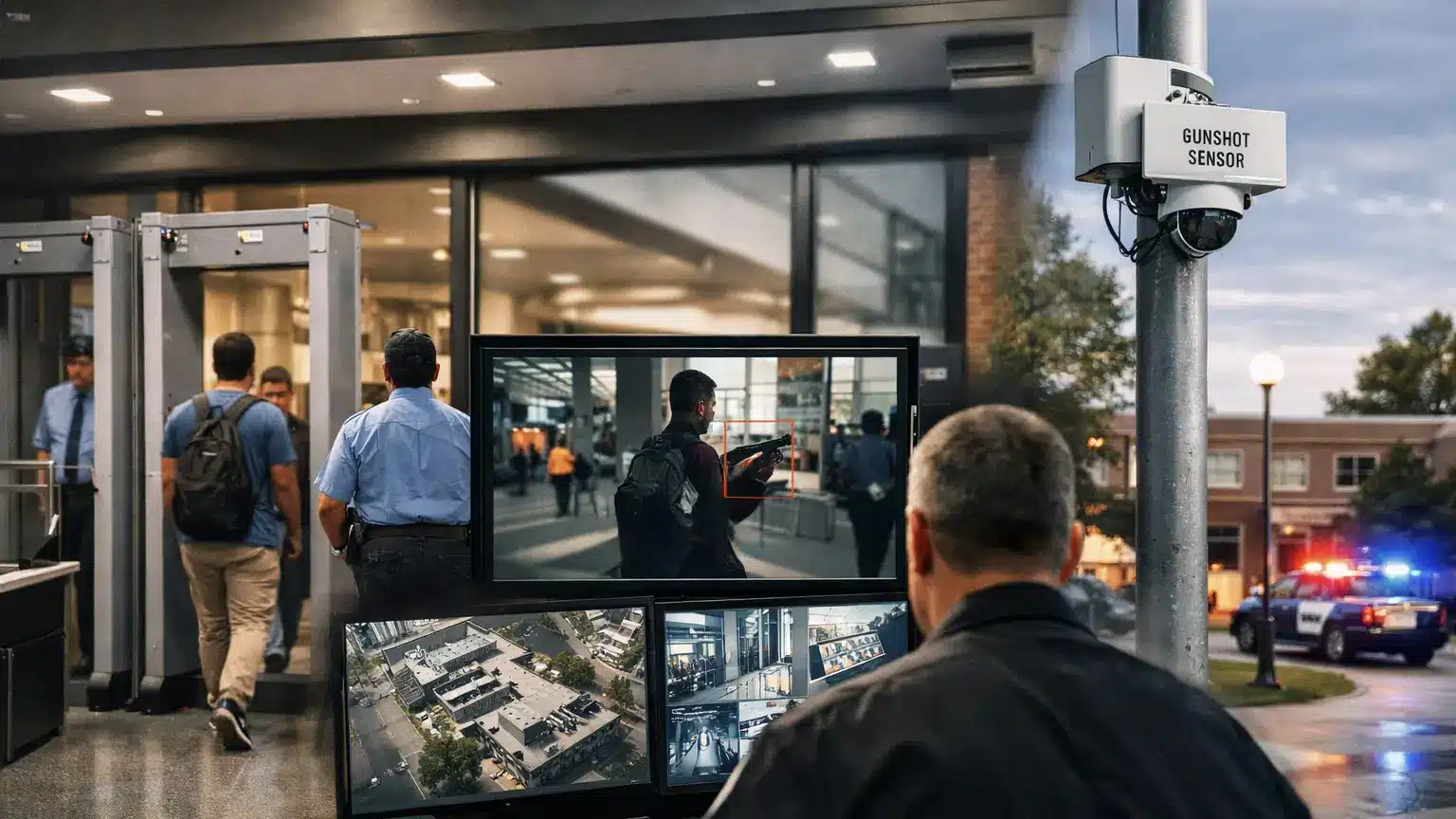
Why “Weapon Detection” Isn’t One-size-fits-all
With hundreds of mass shootings in the U.S. in recent years, happening everywhere from schools to office buildings to retail stores to places of worship, there is growing pressure for these places to invest in good security.
Weapon detection systems like metal detectors, gunshot detectors, AI gun detection technology, and weapon scanners all aim to mitigate the risk of violent attacks by preventing weapons from entering or being used in public spaces. Each solves a different problem: detectors screen entrances, scanners speed that up, AI monitors broader areas for faster response when firearms are brandished, and gunshot detection helps speed up response after a gun has been fired.
They all have their own trade-offs to consider when evaluating a space’s needs. No one solution prevents everything; the goal is risk reduction and coordinated response. Early detection is key to saving lives.
This article looks at these options and the layered strategies for combining them.
Weapon Detection Systems Compared

Before we get started, let’s define what each technology does. These aren’t interchangeable tools… they each serve different purposes in a space’s safety ecosystem.
Concealed Weapons Detection Systems
Metal Detectors
Metal Detectors are electromagnetic devices that alarm when they sense conductive metal mass. They are used at controlled entry points to detect a wide range of metal objects. Walk-through arches and handheld wands have been used for decades everywhere, from airports to schools to event venues. In most cases, they’re used at main entrances and exits to prevent weapons from entering spaces, and people must walk through slowly, removing items like phones, keys, and laptops from their pockets and bags. When the detector beeps, security staff do a secondary search.
Weapon Scanners
Weapon scanners are advanced entry screening systems designed for higher throughput. Many use AI-enhanced sensors to distinguish weapon-like shapes from everyday items like belt buckles and coins. People may walk through without emptying pockets or removing bags, depending on the system settings. These are still “at the door” solutions with a similar experience as traditional metal detectors.
Visual Weapons Detection Systems
AI Gun Detection Technologies
Visual AI Gun Detection systems use computer vision software running on existing security cameras or dedicated cameras to identify visually identifiable firearms in real time, potentially before shots are fired. This technology monitors areas like hallways, public spaces, parking lots, and outdoor areas 24/7. AI gun detection is about campus-wide awareness and response acceleration, not just monitoring at the door.
Audible Weapons Detection Systems
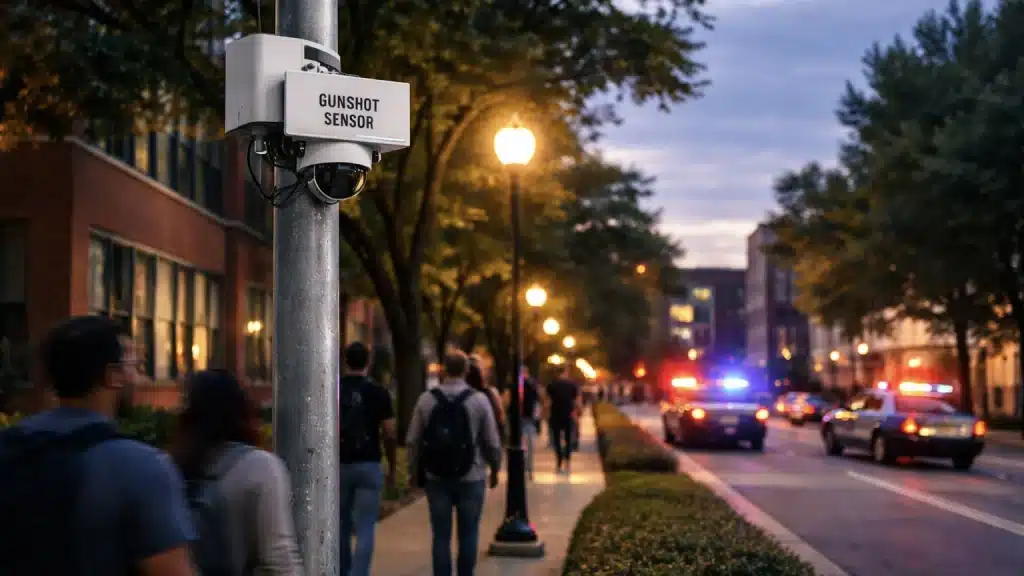
Gunshot detection systems
Gunshot detection systems use strategic acoustic sensors (microphones) to instantly identify and locate the sound of a fired weapon. This technology is for post-event response, providing the shooter’s exact location after the first shot. It doesn’t prevent weapons from entering a space, but eliminates the response delay by sending verified gunshot data to security and first responders, speeding up law enforcement arrival and activation of safety measures like lockdown. Compared to the other technologies, gunshot detection is the least “preventative” option.
Human Video Monitoring
Beyond technology, the most conventional method of weapons detection is human monitoring, where people are in charge of watching live video feeds and identifying threats. Unfortunately, the fatigue that comes from staring at multiple screens for hours on end can lead to missed threats.
While this article focuses on technology, human monitoring will always be the cornerstone of any weapons-detection system. Technology enhances what humans alone can struggle with, like analyzing large amounts of surveillance footage. Studies show that around 95% of screen activity can go unnoticed in just 22 minutes, and this figure worsens the more screens a person is responsible for monitoring. But technology itself is only as strong as the human element… without people to verify alerts and initiate responses, technology becomes useless.
All of these technologies mentioned above can work together as part of a comprehensive security system that includes access control systems, door locks, and emergency communication platforms.
Effectiveness Criteria For Weapon Detection Systems

Technology choices should be based on each organization’s risk profile, campus layout, and operational capacity—not vendor marketing or the latest buzz.
To compare weapons detection technologies fairly, we’ll use five consistent criteria throughout this article, with a focus on what each technology detects.
1. Coverage Scope
What is the purpose of the technology, and what does it actually detect? This evaluates the technology, its effectiveness, and scope. Some tools are limited to a specific area of a building, and others can be scaled across the campus.
2. Throughput & Staffing Impact
This measures the impact the technology has on people flow, considering how many people can move through per minute and how many security staff are required to support the technology. Slower technologies can impact schedules, cause delays, and have a high staffing burden.
3. Detection Ability
This looks at what each technology detects and how well it does it. Does it scan for guns, knives, and/or non-metal threats? Can it detect concealed weapons like a gun in a waistband or visible weapons like a brandished firearm in a hallway?
4. Impact on Experience & Climate
This considers the impact of weapons screening on equity, patron/employee perception, and community trust. If the technology causes long lines, visible checkpoints, and secondary pat-downs, these can negatively impact this.
5. Impact on Response Capacity
Detection is useless if organizations can’t verify, notify, lock down, and coordinate with first responders, including alerting authorities to enhance safety and support response efforts. This looks at the gap between detection and action, where lives are saved or lost.
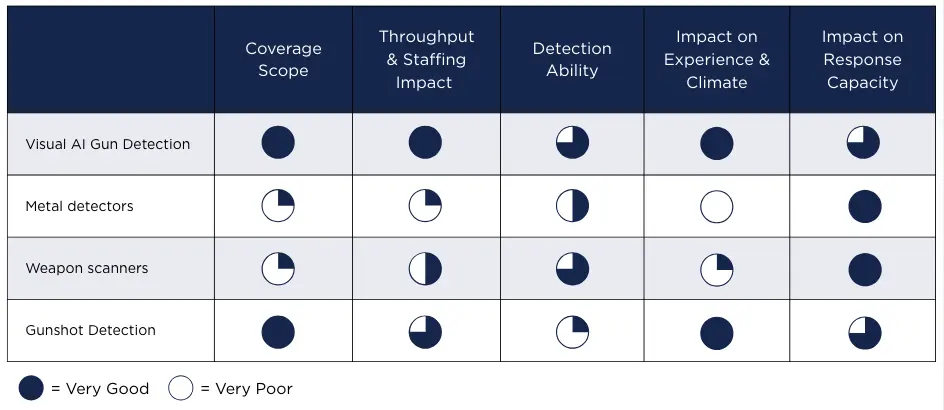
Head-to-Head Comparison of Weapons Detection Technologies

There’s no universally “best” technology. The right choice depends on which risks you’re prioritizing and what operational capacity you have. Here’s how the four options compare across our five criteria:
Coverage Scope
Primary Purpose: The main purpose of both metal detectors and weapons scanners is to prevent weapons from entering a space, whereas AI gun detection functions by detecting bransished firearms that have made their way inside, and gunshot detection systems aim to detect and locate gunshots when a gun is fired, both accelerating response times.
Coverage Area: Metal detectors and weapons scanners are typically placed at building entrances and exits, making their coverage area limited to those spaces. AI gun detection tools can be installed in cameras and gunshot detection systems implemented campus-wide, giving them a much wider and more versatile coverage area. However, they only monitor areas where they are installed, so their coverage is determined by the scale of their installation.
Best Time of Use: Both metal detectors and weapons scanners are most effective when used during arrivals and during events. This is because they can help prevent weapons from entering buildings. Gunshot and visual AI gun detection technologies are best used continually; running 24/7 enables the detection of firearms or gunshots regardless of the time of day, and can catch guns or improve response times to gunshots even outside of regular operation hours or in a layered approach combined with concealed detection systems.
Throughput & Staffing Impact
Throughput Impact: Metal detectors have the greatest impact on throughput of the four. Each metal detector lane has a throughput of about 200-600 people per hour, due to the time it takes for people to remove bags, keys, phones, etc. Weapons scanners are faster, with around 1,200-2,000 people passing through per hour on average. AI gun detection and gunshot detection both have little to no impact on flow as they run in the background and don’t require interaction with passersby or staff.
Staffing Burden: Metal detectors typically have the highest staff burden, as each lane or detector station needs at least two staff members. Weapons scanners have a lesser burden and can be operated with two staff members per lane. AI gun detection and gunshot detection have the least staffing requirements, as they require someone only for verification and monitoring. This can be an existing security person who is trained to identify firearms and evaluate context.
Detection Ability
Detects Concealed Weapons: Metal detectors and weapons scanners can potentially detect concealed weapons, but don’t have a 100% detection rate and often rely on secondary screening methods and configurations. AI gun detection doesn’t possess the ability to detect concealed weapons, and gunshot detection doesn’t detect weapons at all… it enters the conversation when a gun is fired.
Detects Non-Metal Threats: Metal detectors cannot detect non-metal threats, like weapons made from ceramic, plastic, or other materials. Some advanced weapon scanners that combine imaging with analytics aim to improve the detection of concealed non-metal threats, but performance varies widely, and no universal detection rate is established by independent studies. AI gun detection can identify firearm threats, regardless of their material composition, but doesn’t scan for other weapons.
Impact on Experience & Climate
Impact on Climate: Metal detectors can have the highest impact on a space’s climate, with the formation of lines, the enforcement of pat-downs, and the overall perception of places becoming more “prison-like.” Weapon scanners are faster and cause less friction, but still can have a looming presence over visitors and staff. Data-centric AI gun detection and gunshot detection systems have a fairly low impact on an organization’s culture, as they operate invisibly and without bias, mitigating the risk of profiling.
Impact on Response Capacity
Response Capacity: Metal detectors and weapons scanners can both promote immediate response because both require trained security staff to be present during their use. If a weapon is detected, someone can immediately step in to disarm the perpetrator. AI gun detection and gunshot detection tools both help to reduce the response time after a detection is verified.
Typical Failure Models: Metal detectors can fail for a number of reasons, like side door bypasses, nuisance alarm fatigue, and inconsistent use. Weapons scanners can be weakened by protocol lapses and configuration issues. AI gun detection usually encounters issues in low lighting and where there are blind spots. If poorly tuned, staff members can also get alert fatigue and miss actual threats. Gunshot detection systems can miss gunshots in noisy environments or miss low-caliber or suppressed gunshots.
Takeaways
Metal detectors, weapon scanners, and AI gun detection are preventive tools. The first two are best used at controlled doors, but do nothing once someone is inside. AI gun detection is a detect-and-accelerate tool. It doesn’t stop weapons at the door but shortens the time from “gun appears” to “coordinated response.” Gunshot detection is a key tool to help locate where a gun was fired so that all interventions can be targeted. While depending on the organization’s needs, many may benefit from layering multiple technologies.
The Layered Model: Practical Security Stacks For Weapon Detection by Use Case
The most secure places don’t rely on a single technology. They build layered defenses tailored to building type, grade level, and community expectations. Here are a few examples of how security can be layered in different industries.
For Education
Most schools could benefit from adding AI gun detection to their school security systems: It’s non-obtrusive, discreet, low-maintenance, and runs 24/7, making it effective even after hours or during events. Higher-risk districts that have had issues with weapons on campus may also want to layer metal detectors or weapons scanners as well, adding an extra layer of prevention.
Larger campuses like colleges and universities with dozens of buildings and acres of land may benefit from implementing AI gun detection and gunshot detection across campus (indoor and outdoor). Most college campuses are open, so anyone can enter without going through a secure process. Widespread coverage of these two technologies may be able to disarm a threat before it can enter a building and locate it on campus quickly in the event of a crisis. Metal detectors or weapons scanners may be beneficial at building entrances/exits, especially those with high traffic, like sports arenas.
For Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities everywhere can benefit from installing AI gun detection. They are emotional and unpredictable places where conflicts can escalate quickly and put healthcare workers, patients, and visitors at risk. AI gun detection can proactively monitor healthcare centers for firearm threats and give security teams a faster response when presented with one. Higher risk areas may want to have metal detectors or weapon scanners at entrances and exits to prevent weapons from coming in or people from taking potentially harmful tools out.
For Government Buildings
Government facilities range from open public-facing buildings to highly secured environments, like courthouses and legislative offices. Many civic buildings prioritize accessibility, so full entry screening at every door is impractical. AI gun detection provides a discreet, always-on layer of security by monitoring existing cameras in lobbies, hallways, and public service areas. It enhances situational awareness without disrupting public access or increasing staffing, so it’s effective during public meetings, extended hours, and shared use periods.
Higher-risk government facilities often layer preventive screening at main entrances with weapons detection systems like metal detectors or weapons scanners to intercept weapons before entry. AI gun detection complements these tools by monitoring interior spaces and secondary access points so security teams can respond if a firearm appears beyond a checkpoint.
In larger government campuses or outdoor areas, gunshot detection can add value by quickly identifying gunfire and its location. Together, these technologies support a layered approach that balances public access, staff safety, and rapid response.
For Entertainment Venues
Entertainment venues like stadiums, arenas, and concert halls face high-volume crowds and fluctuating risk levels depending on the event. Entry screening is necessary, but must be fast enough to avoid long lines and preserve the guest experience.
Metal detectors or weapons scanners are used at entrances to deter weapons and process large numbers of attendees. These systems are most effective when supported by trained staff, clear bag policies, and well-planned ingress routes.
AI gun detection adds continuous monitoring inside venues, covering concourses, seating areas, restricted zones, and exterior approaches like parking lots. Because it runs in the background, it enhances situational awareness without slowing guest movement.
Gunshot detection can extend coverage to outdoor perimeters and parking structures to help security teams quickly locate gunfire and coordinate with responders. Layering these technologies allows venues to manage access, monitor crowds, and respond rapidly to evolving threats.
Critical Success Factors for All Locations
Technology alone doesn’t save lives. Each location where any technology is used needs:
- Pre-defined workflows: Who verifies alerts? Who has the authority to initiate a lockdown? How is law enforcement contacted? Every organization using any technology for security must have established workflows so everyone knows what their role is, and system failures are reduced.
- Training and drills: FEMA data shows quarterly lockdown drills in schools reduce confusion by 60% during real incidents. Organizations should hold routine training and drills for staff (and students, if a school) to help ensure confidence in the face of a crisis.
- Reunification plans: Reunification plans must be established for staff and other relevant actors to make sure everyone will be accounted for.
- Communication systems: Organizations must implement mass notification systems or ENS to get information out fast during and after a crisis.
- Mental health supports: Early intervention is the best prevention.
Choosing A Technology: Factors Organizations Should Consider
Every organization should know the scope of the technology it is using. Before choosing a weapons detection technology, consider these 7 factors:
- Detection & Performance: Detection of specific threats, performance conditions (lighting, angle), false positives/negatives, 3rd party testing, and uncertainty.
- AI Camera & Infrastructure: Technical requirements for resolution, frame rate, integration with existing or new cameras, processing power, minimum lighting, and handling tricky camera angles.
- Throughput & Staffing (Entry Screening): Realistic throughput in their specific environment, staff needed per lane/shift, training needed, and policy templates for screening.
- Operations & Policy: Playbooks for secondary screening and nuisance alarms, integration with the emergency operations plan, and system behavior during power/network failures.
- Integration & Response: Integration with other systems (access control, PA, radios, mass notification, 911 dispatch), alert delivery methods, and the ability to auto-lockdown.
- Privacy, Data & Compliance: Data retention, access controls, hosting/ownership, use of images for AI training, regulatory compliance, and facial recognition use.
- Support & Lifecycle: Uptime guarantees, software update procedures, warranty, scalability with additional buildings/cameras, and ongoing operational costs.
Conclusions
The debate over AI gun detection vs metal detectors isn’t about finding a winner. It’s about matching technology to risk.
Concealed weapons detection tools, like metal detectors and weapon scanners, reduce risk at the front door, with big throughput and staffing tradeoffs. Visual and audible detectors, like AI gun and gunshot detection technologies, improve organization-wide awareness and accelerate response when a firearm becomes visible or goes off. Neither is a stand-alone security solution.
The most resilient strategy is usually layered: physical access control, entry screening where it makes sense, AI gun detection for continuous monitoring, and strong emergency response plans that tie everything together.
To choose the right technology for your organization, start by mapping your risks. How many entrances do you have? What’s your staffing capacity? Where do visitors and staff move throughout the day? What happens after hours? Then pick the mix of tools that fits those realities. When it comes to weapons detection, choose solutions that combine detection with clear, fast incident workflows. An alert only matters if it triggers action in seconds. Look for systems that turn detection into verification, notification, lockdown, and dispatch integration—all before it gets out of hand.
That’s the difference between technology that sounds good and technology that works.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a weapons detection system?
A weapons detection system is a technology solution that uses tools such as computer vision, artificial intelligence, sensors, or scanners to identify the presence of weapons—like firearms or knives—in real time. These systems are designed to detect potential threats early in places such as schools, workplaces, hospitals, and public venues, enabling faster alerts and response to help prevent violence and improve overall safety.
Which weapons detection technology requires the most maintenance?
Concealed weapons detection technologies, like metal detectors or weapons scanners, are very high-maintenance and require 2+ people to manage them. Audible weapons detection (gunshot detection) requires network integration and physical installation, but has lower long-term maintenance. Visual weapons detection (AI gun detection) is very low maintenance, as they run 24/7 in the background and only require intervention when a detection is verified.
Does any weapons detection technology completely prevent violence?
No. No single technology can prevent all violent incidents. Weapons detection systems are designed to reduce risk, not eliminate it. Entry screening tools prevent weapons from entering controlled spaces, while AI gun detection and gunshot detection focus on faster awareness and response once a threat appears or a shot is fired. The most effective approach is layered: combining prevention, detection, and response with training, policies, and communication plans.
Can these systems replace on-site security staff?
No. Weapons detection technologies are force multipliers, not replacements for trained personnel. Entry screening systems require staff to operate equipment and handle secondary screening. AI gun detection and gunshot detection still require people to verify alerts, make decisions, initiate lockdowns, and coordinate with first responders. Technology works best when it supports well-trained staff with clear workflows and authority to act quickly.
How should organizations think about privacy and community trust when it comes to weapons detection systems?
Privacy considerations vary by technology. Entry screening is highly visible and can impact perception and equity if not implemented carefully. Camera-based AI gun detection typically focuses on detecting objects (firearms), not individuals, and many systems operate without facial recognition. Gunshot detection analyzes sound, not conversations. Organizations should evaluate data retention policies, access controls, and transparency practices, and communicate clearly with their community about how systems work and why they’re being used.



