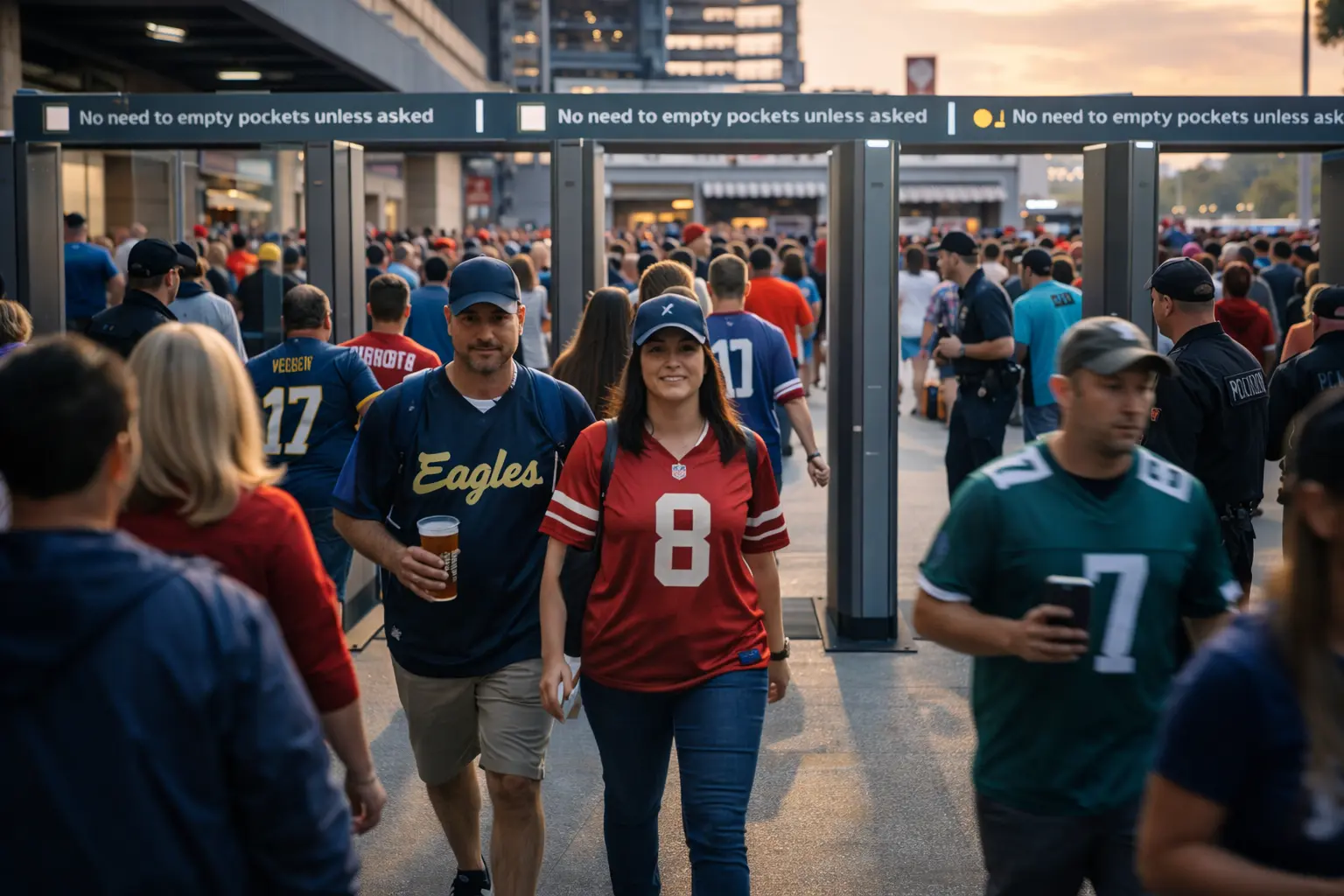
Concealed weapons detection has changed a lot in the last few years. Instead of slow, stop-and-search checkpoints (and metal detectors that scream at belt buckles and keychains), modern systems can quietly screen people as they walk in, spotting firearms, knives, and even explosive threats without forcing everyone to empty pockets, remove coats, or queue up for a pat-down.
In this guide, we’ll break down what concealed weapons detection systems actually are, how they work, and what “good” looks like in the real world: crowd throughput, accuracy, focus-of-attention alerts, privacy considerations, and how these platforms plug into the rest of a security stack like video management and access control. We’ll also cover the realities – no solution is perfect – so you’ll see where the technology shines, where it has limits, and why pairing it with trained security staff and sensible policies is the best way to build safer schools, stadiums, workplaces, and public buildings.
If you’re evaluating options or trying to understand whether these systems fit your environment, you’re in the right place. Let’s get into what you need to know.
Key Takeaways
- Concealed weapons detection systems use artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and cameras to identify guns, knives, and bombs without making people empty their pockets or lift their shirts.
- The best systems can scan large crowds – over 3000 people an hour – and still work without slowing people down. They’re perfect for schools, sports stadiums, corporations and government buildings.
- The top systems meet Homeland Security guidelines, keep a record of all banned items, and work well with other security systems like video management and access control.
- Visual AI gun detection can complement entry screening by using existing security cameras to detect a visible firearm in real time in areas beyond the checkpoint (like hallways, lobbies, and parking/perimeter zones).
What is a Concealed Weapons Detection System?
A concealed weapons detection system is a sensor- and AI-driven security solution that detects concealed firearms, metallic weapons, knives, and sometimes explosives as people walk through entrances at a faster pace than traditional metal detectors. These systems are a big departure from older methods because they can spot threats without completely pausing all traffic or requiring intrusive searches to find the location of the object of interest.
Unlike traditional metal detectors that trigger alarms at anything metal – keys, belt buckles, phones – modern concealed weapons detection systems use object recognition to be able to distinguish between a weapon and a phone. This helps reduce false alarms and minimizes the need for a second screening.
You can find these systems in:
- K-12 schools and universities
- Sports stadiums and concert venues
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Police stations and municipal buildings
- Corporate headquarters and data centers
- Government buildings and critical infrastructure
Since about 2020, systems used in North America have been able to screen up to 3,600 people per hour per lane. This is fast enough for busy entrances where traditional checkpoints would cause long delays. While these new systems have made significant strides over traditional metal detectors, like any advanced security technology, concealed weapons detection systems have important limitations that organizations should understand before deployment.
Limitations of Concealed Weapons Detection Systems
While concealed weapons detection systems have their advantages over traditional methods, there are limitations that need to be addressed to ensure responsible use of the technology.
No system delivers perfect accuracy.
AI-based concealed weapons detection systems struggle to find the right balance between false alarms and missed detections. If a system is set to be more sensitive to detect more concealed weapons, it will trigger many false alarms. If it’s made less sensitive to reduce false alarms, it may miss some concealed weapons.
Accuracy is a major challenge for AI-based concealed weapons detection systems. It is difficult to balance the false positive and false negative rates of the system. If the system is made more sensitive to detect more concealed weapons, it may start detecting false alarms. On the other hand, if the system is made less sensitive to avoid false alarms, it may start missing some concealed weapons. Recently, the issue of accuracy came under the spotlight of various governments and regulatory bodies. It was found that the accuracy of some of the systems was not as claimed by the vendors.
Detection capabilities vary by weapon type.
Many concealed weapons detection systems are designed mainly for firearms. They may not detect smaller weapons, improvised objects, ceramic blades, or items made to avoid detection as consistently. You should consider which types of threats are most relevant to your situation and check the system’s capabilities accordingly.
Environmental and operational factors affect performance.
The system’s effectiveness depends on real-world conditions. High crowd density, poor lighting, reflective surfaces, electromagnetic interference, weather conditions, and improper sensor placement can all reduce detection accuracy. Performance may also vary based on clothing layers, body positioning, and how an object is concealed. Proper installation, calibration, and ongoing testing are critical
Human oversight remains essential.
Concealed weapons detection systems help trained staff make decisions, but they should not replace human oversight. When an alert occurs, someone must review it, use their judgment, and follow response procedures. Without clear protocols and trained personnel, there is a risk of overreacting, delaying responses, or enforcing rules inconsistently.
Privacy and perception considerations must be addressed.
It’s also important to consider privacy and how people perceive these systems. Even when systems don’t store images or use facial recognition, they can still raise privacy concerns among employees, students, or visitors. Being clear about how the technology works, what data is collected, and how alerts are managed is crucial for building trust and ensuring compliance.
Effectiveness depends on integration with broader security strategies.
Concealed weapons detection systems are most effective when used with other safety measures. These include controlling access, evaluating behaviors that may pose a threat, communicating during emergencies, and providing training and planning for incidents. Relying only on detection technology can lead to a false sense of security.
There is no universal performance standard.
Performance can vary by vendor, setup, and environment. Some systems may meet government or industry guidelines, but there is no federal certification or benchmark that works in every situation. Always check claims by running pilot tests, evaluations, and learning from real-world experiences.
How Concealed Weapons Detection Systems Work
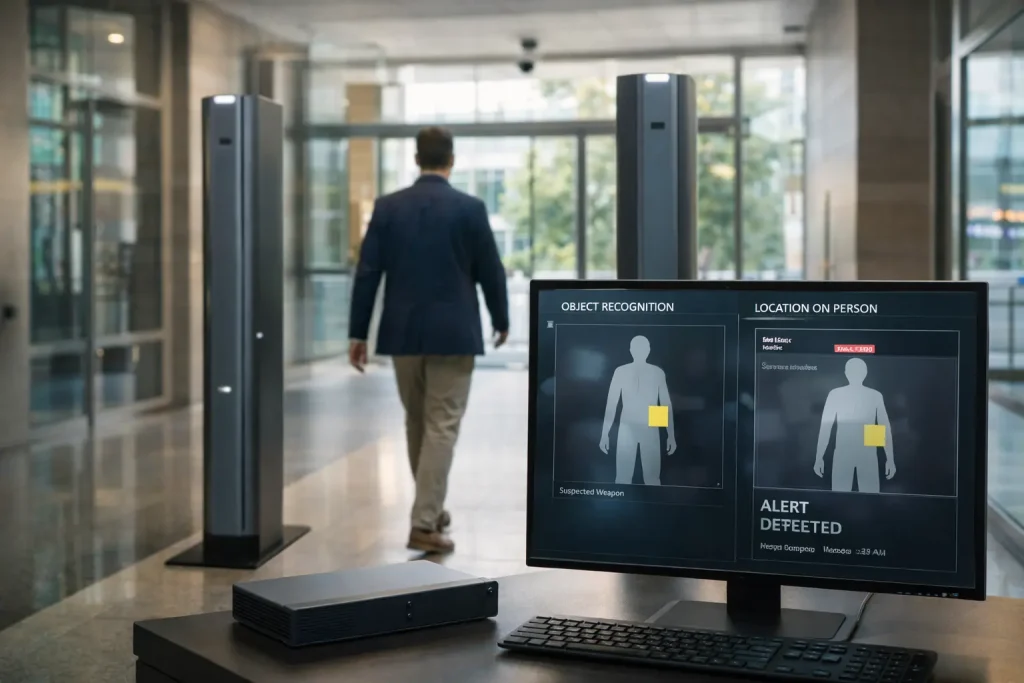

Today’s concealed weapons detection systems use several technologies to find threats in real time. They use sensing methods like electromagnetic fields, 3D imaging and AI trained on large weapon datasets. This allows the system to recognize weapons rather than just the presence of metal.
Core System Components
A typical system includes several elements that work together:
- Sensors or panels: Generate electromagnetic fields and capture return signals
- Cameras: Show the security team what’s going on
- AI processing unit: Analyzes what the sensors and cameras have found
- Network connection: Links to the other security systems and the main monitoring system
Threat Object Recognition
The main difference between concealed weapons detection systems and traditional metal detectors is how it interprets data. Instead of detecting all metal objects, AI models focus on specific signs linked to guns, knives, and other threats.
When a person walks through at a normal pace, the system:
- Captures electromagnetic and visual data
- Uses its AI to process information
- Checks if detected objects match threat profiles.
- Generates alerts with specific information on where the weapon is located
This processing takes just milliseconds, so people can walk through without stopping. When security detects a threat, operators receive alerts with images showing exactly where the suspicious object is on the person or in the bag.
Data Logging and Audit Support
The top systems record every event, including the time, lane, alarm level, captured images, and resolution status. This information helps with compliance reports, investigations after incidents, and analyzing trends to spot ongoing security patterns.
Key Features and Capabilities
When looking for concealed weapons detection systems, security teams should look for key features that set advanced systems apart from basic equipment. Advanced systems can automatically alert security personnel or response teams when they detect a threat. This ensures quick and clear communication for a fast response.
High Throughput and Multi-Lane Support
For venues that process hundreds of thousands of people, volume capacity matters. For example, a major league baseball stadium or a large high school needs to be able to screen people quickly to prevent bottlenecks.
Considerations include:
- The number of people that can pass through one lane in an hour
- The capacity to handle two-way traffic
Touchless, Frictionless Screening
These systems can scan without making people take off their coats, empty their pockets or remove their bags. This is a big advantage, as it reduces queue times, keeps them moving and decreases staff workload.
Focus-of-Attention Alerts
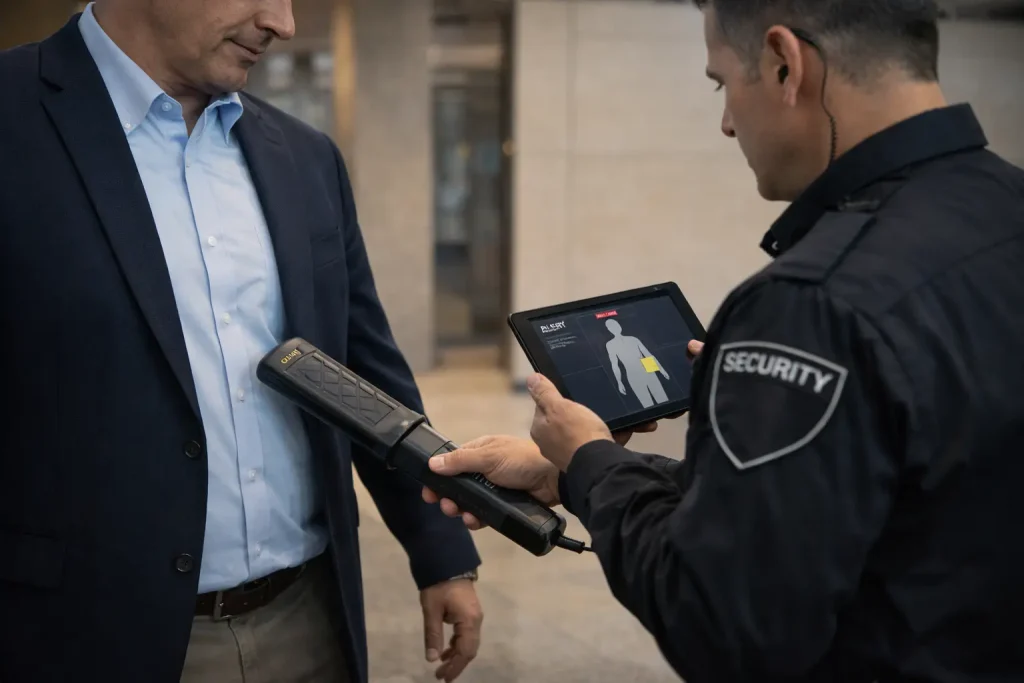

When the system spots a threat, security operators get a visual alert on exactly where the suspicious item is. This accuracy means that instead of conducting a full-body search, staff can do a targeted secondary check. This helps to improve the process and make it more efficient for the person being screened.
Sensitivity Settings
Advanced systems offer multiple sensitivity profiles – often five or more levels. This lets administrators fine-tune detection performance for different environments:
- Elementary schools may prioritize minimal disruption
- Government buildings may require maximum sensitivity to detect various weapon sizes
- Event venues may adjust settings based on what they know about upcoming threats
Integration Capabilities
Modern concealed weapons detection systems connect with larger security networks, including:
- Video management systems for bookmark links to events
- Access control systems that use credentials for response workflows.
- Incident management tools to automate incident reports and procedures
- Central monitoring stations for remote verification and response
Deployment Flexibility
Organizations need options for permanent and temporary installations:
- Indoor-rated systems for lobbies and entrances
- Outdoor units that can handle harsh weather for stadium gates and exterior checkpoints
- Portable versions on wheels for events or high-risk periods
Visitor Experience
The goal of concealed weapons detection systems is to improve security while maintaining a smooth experience for legitimate visitors, students, employees and guests.
Walk-Through at a Comfortable Pace
Unlike some other security setups that require people to stop and empty their pockets, modern concealed weapons detection systems let people walk side-by-side, carry backpacks, and keep personal items in their pockets. This “walk at normal pace” operation mirrors everyday building entry rather than airport-style screening.
Benefits include:
- Students getting to school on time without long lines
- Staff changes without long wait times
- Getting to your seat before the game without being stuck in line at the stadium
- Corporate lobby security that doesn’t slow down business operations
Reducing Second Screenings
These systems help identify real threats and harmless items, which greatly decreases the number of people who need pat-downs or bag checks. When secondary screening is necessary, focus alerts speed up and target the process.
Privacy and Dignity
Modern concealed weapons detection systems focus on finding dangerous objects instead of using body scans, which raise privacy concerns. Current platforms do not produce body images and keep only data that is relevant to an event, including timestamps, alert images and resolution status.
Communication and Signage
Effective deployments should have clear signs and messages at the entrance to help visitors know what to expect.
- Signs that explain the screening process
- Digital displays that show the system’s status
- Scripts for security to follow when answering questions
- Clear messaging: “No need to empty your pockets unless we ask you to”
Compliance, Documentation, and DHS-Aligned Best Practices
Concealed weapons detection systems now follow guidelines from the Department of Homeland Security for security at entryways and record-keeping.
Keeping Track of the Items That Get Flagged
Well-designed systems keep a record of all prohibited items, including:
- What the item was (and what type it was)
- Where on the person or bag it was
- Date, time and lane ID
- Images from the event
- Resolution status and what actions were taken
This approach mirrors the DHS’s recommended documentation practices, which help improve operations and provide legal support.
Automated Testing and Compliance Records
Organizations that need to run periodic tests can benefit from software that automates tasks and records results. The records include:
- Test date, time and location
- Test object that was used
- Pass/fail status
- Operator ID
- System settings at time of test
These records show that you are keeping up with requirements and help spot any decline in system performance over time.
Real-Time Notification Workflows
When an item is confirmed by security personnel, the system should send instant notifications to supervisors and security operations centers (SOCs). Messages should be sent through multiple channels, including:
- Video management system alerts with linked footage
- Access control system integration for lockdown procedures
- Mobile app push notifications to responding officers
- Radio dispatch integration for immediate response
These notifications help security teams react quickly.
Trend Analysis and Operational Insights
Structured data collection helps organizations find patterns and improve their security. Look for common trouble spots, time-of-day patterns, trends in detected items and staff alignment with actual threat activity.
Legal Defense
Clear digital records of alarms, secondary checks and results help organizations show they take security seriously. When incidents happen or policies are challenged, detailed documentation supports the organization’s claim they had the right security measures in place and used them correctly.
Using Concealed Weapons Detection in Different Places
The same concealed weapons detection system can be used in different environments, each with its own challenges and threats.
Schools: K-12 and Universities
There were more than 230 school shootings in 2025. As a result, schools are one of the fastest-growing segments for concealed weapons detection systems. They typically install them at main entry points, athletic facilities, auditoriums and administrative building entrances.
In educational environments, the focus is on getting students, staff and visitors through quickly during short arrival windows (typically 15-30 minutes), with minimal disruption to flow, and an age-appropriate process that doesn’t create an intimidating environment.
Stadiums and Entertainment Venues
Over the past several years, professional sports venues and performing arts centers have increased the use of concealed weapons detection systems. This is driven by capacity needs, fan experience concerns, insurance and liability considerations, as well as league and security requirements.
Stadiums often use multi-lane setups at each entrance. They also connect to ticketing systems and have staffing plans that adjust based on attendance.
Corporate and Critical Infrastructure
An increase in workplace violence has driven deployment at corporate headquarters, manufacturing facilities, and critical infrastructure sites. According to a report from Traliant, an HR compliance training company, approximately 25% of employees reported witnessing workplace violence in the past five years. That number jumped to 30% in 2025.
A concealed weapons detection system deployment includes:
- Employee screening at the main entrance or secure areas
- Integration with badge-based access control systems
- Visitor management connections
- Alignment with HR policies and legal workplace safety programs
Government and Justice Facilities
Courthouses, municipal buildings and police stations are looking to upgrade their traditional metal detector checkpoints while still maintaining threat detection requirements. These environments often require:
- Maximum sensitivity settings
- Detailed records for court cases
- Integration with existing security systems
- Coverage for both public and employee access points
Temporary and Event-Based Deployments
Portable concealed weapons detection systems have become popular for short-term high-risk situations like conferences, conventions, outdoor festivals, community events, graduation ceremonies and periods of heightened threat awareness.
These portable systems can roll in and out on wheeled bases or trusses without having to be installed permanently.
System Integration and Orchestration
Concealed weapons detection is most effective when part of a larger security system rather than just a separate checkpoint. Increasingly, that “larger system” also includes visual AI gun detection on existing security cameras, so teams can detect threats beyond entry lanes and automatically trigger emergency notification and response workflows.
Video Platform Integration
When an alarm is generated, integration with video management software allows you to:
- Bookmark video clips associated with the alarm
- Link video directly from the alarm event
- Review the video for verification
- Export evidence for law enforcement or legal proceedings
Orchestration and Workflow Automation
Modern security platforms can automatically handle detection events by
- Creating task lists in management systems
- Assigning tasks to security personnel based on their location
- Guiding operators through standard operating procedures
- Escalating unresolved alarms to supervisors
- Logging response times and actions taken
Access Control Integration
Linking concealed weapons detection systems to access control systems enables:
- Locking doors when an alarm is triggered
- Credential-based screening exemptions for authorized personnel
- Watchlist integration for closer monitoring of specific individuals
- Automated alerts for access attempts after detection events
Centralized Data Repository
Enterprise set-ups benefit from storing all alarm events, testing records, prohibited items, performance metrics and cross-site analytics in one place.
Safety, Health, and Tech Considerations
The safety of people remains a top priority, and these systems are engineered to meet electromagnetic safety and medical device compatibility standards.
Electromagnetic Safety
Low-frequency electromagnetic technology used in many concealed weapons detection systems has been tested and is generally considered safe for:
- Pregnant women
- Children of all ages
- People with pacemakers or implanted cardiac defibrillators
- Individuals with other medical implants
- People with cochlear implants or insulin pumps
Organizations should verify that their systems meet relevant EMC standards and get test reports during the evaluation process.
AI Model Performance
Detection capability depends on the quality and refinement of AI models. Key factors for performance include:
- Validated detection rates for firearms of various sizes
- Detection of knives and other edged weapons
- False alarm rates under real-world conditions
- Performance with concealed items in bags vs on the body
- Effectiveness across different clothing and body types
Periodic Re-Testing
Companies should establish regular, realistic testing protocols to verify system performance. Detection rates can be affected by:
- Environmental factors (temperature, humidity, electromagnetic interference)
- Software updates and model changes
- Physical wear or damage to sensor components
- Changes in threat landscape or concealment methods
Important Limitations
No concealed weapons detection system is 100% accurate. Companies should:
- Pair tech with trained security staff doing secondary screening
- Put in layered security measures
- Develop and test response protocols for various threat scenarios
- Remember that determined adversaries may try to beat the system
Incident Response and Management
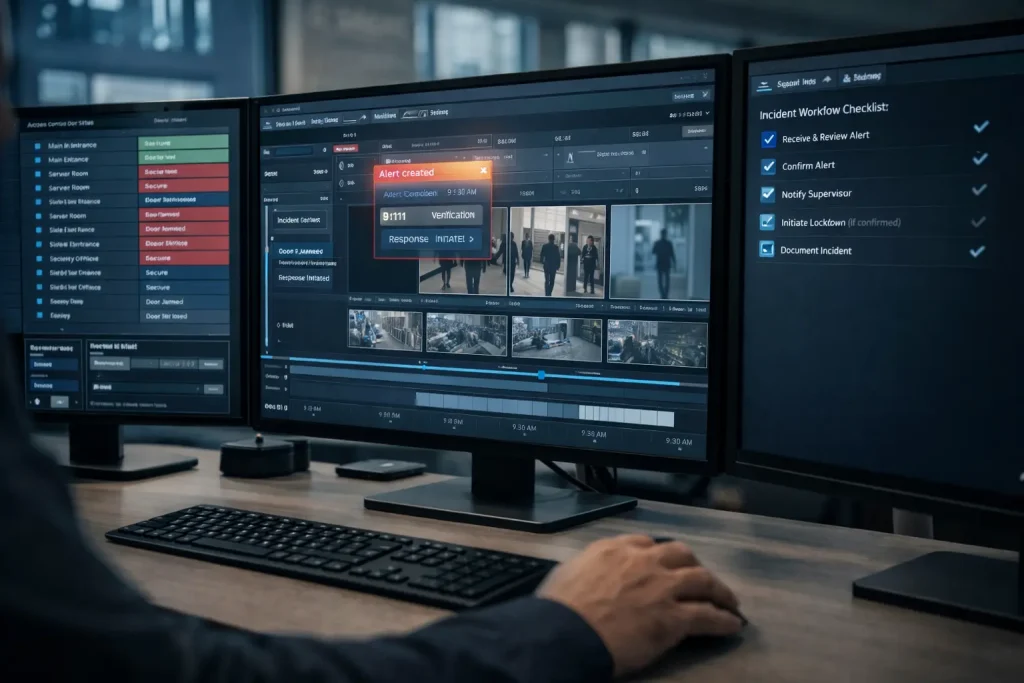
A robust incident response plan is critical to get the most out of any concealed weapons detection system – and for keeping everyone in the facility safe. So, when a potential threat is picked up, security personnel must be prepared and ready to act fast. That starts with comprehensive training for the security team, so they know what the alerts mean and can respond with confidence.
Integrating concealed weapons detection systems with other security systems is key to a coordinated response. When an alert is triggered, security operators should get real-time notifications, so they can quickly assess the situation and respond. This might involve lockdown procedures, directing security staff to specific locations, or contacting law enforcement if needed.
Regular testing and training exercises are essential to stay prepared. By practicing real-world scenarios, security teams can find weaknesses in their response plans and improve how they handle incidents with hidden weapons. These exercises also ensure everyone, from managers to security staff, knows what to do during an incident.
Responding to an incident isn’t just about reacting quickly; it’s about keeping everyone informed throughout the whole process. Whether it’s the administrators, security staff, or law enforcement, everyone needs to know what’s going on from start to finish.
After any incident, a review can help identify what was learned and areas for improvement. This feedback helps systems continue to evolve with new threats and maintain high safety and efficiency.
System Maintenance and Upgrades
Keeping the concealed weapons detection system in top shape is crucial for smooth security operations. Regular maintenance checks – including checking the hardware and software – prevent false alarms and keep the system running smoothly so it’s always ready to detect concealed weapons and other threats.
Create a schedule for routine checks – test sensors, review alert logs, update AI algorithms. As new threats emerge, software updates and AI improvements help the system adapt and maintain high detection rates.
Support and training are important for security personnel. They need to stay up to date on new features, best practices and troubleshooting methods to use the system effectively. Many organizations work with their solution providers to hold regular training sessions and provide technical support. This ensures their teams can handle any issues that arise during operations.
A well-maintained concealed weapons detection system not only keeps breaches at bay but also creates a safe and welcoming environment for everyone in the building. Proactive maintenance and upgrades help organizations protect against hidden threats, stay compliant with industry standards and keep their security system reliable as technology and threats evolve.
Choosing and Evaluating a Concealed Weapons Detection System
When looking for a concealed weapons detection system, take a structured approach. Also consider the financial health and prospects of the company providing the system. Look at sales numbers, growth rates and predictions for the future. This will ensure the vendor is strong in the market.
Detection Performance Criteria
Evaluate the system against specific threats that are relevant to your environment:
- Firearms – detection rate for handguns, long guns and compact weapons
- Knives – performance with various blade lengths and materials
- Improvised explosive devices – ability to identify explosive materials and components
- Non-metallic threats – detection of ceramic knives, 3D-printed weapons
Operational Requirements
Practical factors that will affect daily life are also worth considering:
- Throughput needs: How many people will be coming and going at the same time?
- Indoor/outdoor rating: What’s the environmental protection needed for the spot where it’s going?
- Footprint and lane width: Will it actually fit in the space available?
- Portability: Is it easy to move around if necessary?
- Power and network: Is the infrastructure and power supply available?
- Installation timeline: How long is the deployment going to take – hours vs. days
Software Capabilities
Looking at the management and reporting features of the platform is also key:
- Operator and supervisor interface: Are the dashboards user-friendly?
- Remote control: Can it be controlled remotely for multi-site deployments?
- Role-based access control: Is there admin access control?
- Reporting: Are there reporting tools for compliance and analytics?
- Export data: Available for auditors, insurers, or the legal team
Pilot Testing
Before full deployment, test it during real-world operating hours, for example:
- School morning arrivals
- Stadium gate operations before an event
- Shift changes at facilities
- Peak lobby traffic at corporate buildings
Measure real-world performance, including line length, staff workload, visitor feedback and detection accuracy.
Total Cost of Ownership
Create a detailed cost model that includes:
- Hardware costs (or leasing fees)
- Software licensing (often annual subscriptions)
- Installation and integration services
- Staffing changes (increases or decreases)
- Training for security operators
- Ongoing maintenance and support
- Technology refresh cycles (usually 5 or 7 years)
Future Developments: Beyond Entryways with Visual AI Gun Detection
The future of concealed weapons detection is being shaped by rapid technology advances – and it promises to bring a whole new level of security and efficiency to organizations worldwide.
Concealed weapons detection is great for controlled entry points, but not every risk starts at a lane. Visual AI gun detection expands protection by turning existing security cameras into an early-warning layer that can detect a visible firearm in seconds, including in outdoor areas and large open spaces where traditional entry screening can’t help.
Since visual AI gun detection can integrate with most existing IP camera environments, it can be deployed quickly across campuses, parking areas, perimeter zones and high-traffic interiors without a major camera replacement project, making it a good option for organizations that want to add coverage fast.
Pairing AI Detection with Emergency Notification for Faster, Coordinated Response
Omnilert pairs AI gun detection with an integrated Emergency Notification System (ENS) and automated response workflows, so once a potential threat is identified (and verified), organizations can send multi-channel alerts and activate a coordinated, facility-wide response. This reduces the time between “first sighting” and “everyone who needs to know, knows,” including staff, security teams, and law enforcement, so the response is faster, clearer, and more consistent.
This is what a true end-to-end strategy looks like: prevention + notification + engagement + incident management working together, rather than disconnected tools that leave teams stitching together the response in the most critical moments
And because real-world environments are messy (lighting changes, angles vary, crowds move), the most effective solutions are built to perform in real conditions. Omnilert uses a data-centric AI approach trained and refined with diverse, real-world data to improve reliability and reduce false alerts over time.
As threats get more complex, organizations need to invest in the latest technology. By adopting new tools, like AI-enabled detection paired with automated emergency notification and response, organizations can protect their facilities, staff, and visitors now and in the future.
Learn how Omnilert helps detect threats faster and coordinate response with visual AI gun detection and emergency notification. Contact us to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Concealed Weapons Detection System?
A concealed weapons detection system is a security technology designed to identify firearms or other weapons hidden under clothing or in bags without requiring physical searches or metal detector walkthroughs. These systems typically use advanced sensors—such as millimeter-wave imaging, AI-powered video analytics, or radar-based scanning—to detect the shape, density, or signature of a weapon in real time as people move naturally through a space. The goal is to provide early threat detection while maintaining high throughput, reducing friction for occupants, and enabling security teams to respond quickly before a weapon can be used.
Do visitors need to remove phones, keys and bags when walking through concealed weapons detection systems?
Most modern entry screening systems are smart enough that you can keep your phone, keys, wallet and bags in your pockets and handbags. The AI in them can tell the difference between the usual carry items and actual weapons. Only the people who trigger an alert will need to have a closer look – and even then, the system helps the security staff know who to focus on rather than having to do a full search.
Where are concealed weapons detection systems usually installed?
You’ll often see them at main school and university entrances, stadium and arena gates, hospital ER entrances, courthouse public access points, company lobby checkpoints, government building entrances and event venue gates. Organizations focus on high-traffic areas and places where the risk is highest. Visual AI gun detection is used in areas covered by security cameras, like hallways, lobbies, parking areas and perimeters where you’re not running people through a screening lane.
What data do these systems store, and how long is it kept for?
They typically store event logs (time, scanner, type of alert), any imagery from the time it raised an alert, testing records and what the security team did about it. Modern systems don’t store any detailed images, and the data is kept for a month to three months, depending on what the organization needs for a particular incident. Visual AI gun detection systems may also generate alert records tied to camera events and retention depends on the organization’s policies and the platform configuration.
Are there regulatory requirements or certifications for concealed weapons detection systems?
There isn’t a single federal requirement for most venues, but a lot of organizations follow the DHS guidelines for entryway security, which means they need to document the testing they do, what happened with any prohibited items and how they respond to incidents. They should also make sure the system they choose meets certain standards for electromagnetic emissions – and in some places, there may be specific rules for schools or government buildings.
Is visual AI gun detection the same thing as concealed weapons detection?
No, visual AI gun detection and concealed weapons detection are different applications to solve similar problems. Concealed weapons detection is used to screen the entry doors of organizations. Sensors and AI work together to find a concealed weapon that the person may be carrying as they walk through the pathway. Visual AI gun detection, on the other hand, is meant to monitor security feeds to identify if the person is holding a visible firearm in areas such as hallways, parking lots, etc.



